🇫🇷 Lire en Français | 🇪🇸Leer en Español | 🇧🇷Leia em português
During a recent Q&A webinar, a rather unique question caught my attention: “How do you manage premature puppies?” This isn’t a topic we often discuss – yet I believe it’s vital. Premature puppies are those born before their gestation period is complete, typically showing less developed physical features and requiring immediate and special care. Realizing the importance and breadth of information needed to tackle this subject, I decided to dig deeper and share insights through this blog. Here, we’ll explore everything from the signs of premature delivery to the careful nurturing these fragile lives demand.
- What Are the Signs and Causes of Premature Puppy Birth?
- How Can You Care for a Premature Puppy?
- How Can Veterinary Interventions Help With Premature Puppy Deliveries?
What Are the Signs and Causes of Premature Puppy Birth?

What exactly constitutes a premature newborn puppy?
Unlike their fully developed counterparts born after a normal gestational period of about 63 days, premature puppies come into the world earlier, significantly underdeveloped and not fully prepared to face life outside the womb.
These puppies often struggle with numerous developmental issues, most notably their inability to breathe effectively. This breathing difficulty stems from a lack of surfactant—a substance crucial for healthy lung function.
Surfactant is a fatty protein essential for reducing surface tension within the lungs, allowing them to expand and contract effectively during breathing.
Without sufficient levels of surfactant, the lungs of newborn puppies may collapse upon themselves, making it extremely difficult for the puppies to breathe on their own.
This is a critical condition known as Respiratory Distress Syndrome in human neonatal medicine, where premature births are similarly challenging.
Interestingly, studies on canine gestation have shown that surfactant is present in puppies around 58 days post-ovulation. This timing is crucial because puppies born before this gestational milestone have not yet begun to produce surfactant naturally, which severely impacts their ability to breathe if born too early.
In human medicine, advancements have led to the creation and use of synthetic surfactants which can be administered to premature babies to assist with their lung function until they can produce their own. Unfortunately, such medical interventions have not yet crossed over into veterinary practice. There is currently no synthetic surfactant available for premature puppies, which means that those born before the 58-day mark face a grim prognosis.
Identifying Early Labor in Dogs

If the prognosis is grim for puppies born before 58 days of gestation, those born after 58 days but before the normal parturition day are also considered premature.
The occurrence of such early deliveries is often referred to as early labor.
Understanding and identifying early labor is critical for dog breeders, as it directly impacts the health and viability of newborn puppies.
From a practical standpoint, one of the most effective strategies for dog breeders is to pinpoint the expected date of parturition in the female dog.
This allows for better preparation and immediate intervention if premature labor occurs.
The most reliable method to predict the day of parturition, in my opinion, is to conduct a timing of ovulation using progesterone tests at the time of breeding.
Knowing the exact day of ovulation can significantly enhance the accuracy of predicting the parturition date.
And research indicates that the length of pregnancy in dogs can vary depending on the breed size.
For instance:
– In small dogs, the gestation period is typically around 62 ± 1 days post-ovulation.
– In medium and large dogs, it’s generally around 63 ± 1 days post-ovulation.
– In giant dogs, the duration extends to about 64 ± 1 days post-ovulation.
Therefore, timing ovulation during the breeding season is a crucial practice.
Not only does it optimize fertility and potentially increase litter size, but it also plays a pivotal role in identifying and managing cases of premature labor.
This proactive approach allows breeders to prepare for the special needs of premature puppies, including immediate veterinary intervention and specialized care to improve their survival chances.

I am on a mission to learn everything about dog and cat breeding. Sign up to my newsletter to follow my journey, and receive exclusive content and offers!
Common Causes of Premature Birth & Risk Factors for Premature Puppies
It’s crucial to be aware of the common causes of premature birth in dogs because, here once again, prevention is key. Understanding these factors can help breeders and pet owners take proactive measures to reduce the risk of early labor.
| Genetic Factors | Some breeds or individual dogs may have a genetic predisposition to premature labor. | Prevention Tip: When working on the genetics of the individuals selected for breeding, reproductive traits should always be taken into account, and gestation length should be one of them. If there is a recurrent history of early labor in a given line, this line should not be considered for breeding. Checking genetic diversity is also an important element as low genetic diversity is associated with more reproductive disorders. |
| Infections | Any infection happening during gestation could lead to early labor. | Prevention Tip: Checking status for canine brucellosis is recommended before breeding. Making sure the female is up to date with her vaccines before breeding is always helpful as well. |
| Nutritional Deficiencies | Proper nutrition is vital for a healthy pregnancy. Deficiencies can lead to developmental problems and premature birth. | Prevention Tip: Problems like pregnancy toxemia can lead to early labor. It is therefore important to optimize nutrition during gestation in dogs. Providing a balanced diet that meets all the nutritional needs of a pregnant dog is crucial. |
| Hormonal Imbalances | Luteal failure, where the body doesn’t produce enough progesterone to maintain pregnancy, can be a concern. | Prevention Tip: Monitoring progesterone during gestation is the best way to prevent this. This is typically done only in females which had a history of infertility or early labor, as luteal failure is not common. |
| Physical Stress | Excessive physical activity or trauma can provoke premature labor in pregnant dogs. | Prevention Tip: While not much data exists, the rule of thumb is to avoid overexercising the animal during gestation. What represents overexercise obviously depends from one animal to the other. |
| Environmental Stressors | Stressful environments, including excessive noise, heat, or changes in living conditions, can negatively impact pregnancy duration. | Prevention Tip: The use of pheromones has been described before parturition to improve maternal behavior in females. This can also help appease them and should be considered. Having a dedicated maternity space where they can settle about a week before birth can also reduce stress. |
| Uterine Overcrowding | In cases of large litters, the physical pressure and limited space can lead to early labor. | Prevention Tip: Identifying potential overcrowding in advance is crucial. Taking an X-ray around 50 days into gestation can help identify if there are more puppies than usual, which may prompt early labor. |
| Age of the Mother | Very young or older dogs are at a higher risk of premature delivery, often due to less optimal body conditions and health status. | |
| Chronic Health Issues | Health issues like diabetes or systemic infections can compromise a dog’s ability to carry a pregnancy to term. | Prevention Tip: Adhering to the rule of thumb to only breed individuals that are healthy is key. If the animal has any kind of medical disorders (like diabetes or urinary problems), breeding should be avoided. |
| 👉🏽I believe it is essential for breeders to evaluate the genetic diversity of the dogs they plan to breed, as research has shown that increased genetic diversity enhances reproductive performance, including fertility. Here is the test I recommend for assessing genetic diversity in breeding dogs. |
How Can You Care for a Premature Puppy?

Recognizing a premature puppy can be crucial for immediate care.
A premature puppy often appears significantly smaller and less developed compared to its littermates who are born at full term.
Their skin can be noticeably thinner and may appear almost transparent, lacking the usual puppy fat that provides a rounded appearance.
They might also have a lack of hair or only a fine coating, giving them a more fragile look.
Furthermore, these young pups often struggle with basic instincts and reflexes such as suckling, and they might be noticeably weaker with less vocalization than their healthier counterparts.
Their inability to regulate body temperature effectively makes them more prone to complications if not immediately addressed.
Immediate Steps to Take Post-Birth

When a premature puppy is born, every moment counts, and the actions taken immediately after birth can significantly impact their chances of survival.
Here are the critical initial steps to optimize their care:
1. Resuscitation: This is a crucial step for premature puppies, who might not start breathing immediately after birth. Unlike with full-term newborns, where the mother might sometimes stimulate respiration, intervention by a human is often necessary for preemies. It’s important to gently clear the airways and stimulate breathing using safe techniques.
For detailed guidance, refer to my previous blog on resuscitating newborn puppies:
Preventing Shaken Puppy Syndrome: A Dog Breeder’s Guide

2. Umbilical Cord Care: Handling the umbilical cord with extra care is vital for premature puppies due to their heightened vulnerability to infection and injury. The cord should be cleanly cut and disinfected to prevent complications.
More detailed steps will be covered in my previous blog on this subject:
Essential Puppy Survival Tips: The Newborn Care Step You Can’t Ignore!
3. APGAR Scoring: APGAR scoring helps assess the health of newborn puppies and is especially important for identifying the needs of premature ones. It measures heart rate, respiration, irritability, muscle tone, and color. This quick test is critical in determining whether additional support is needed.
More about how to perform APGAR scoring in this detailed blog post:
The Neonatal Game-Changer: APGAR Scores for Puppies & Kittens
4. Weighing: Premature puppies often have a low birth weight, making it essential to weigh them soon after birth. This not only helps confirm their premature status but also aids in monitoring their growth and health progression accurately.
More info about this in this blog:
You will soon have newborn puppies at home? You will need this for sure.
| Breed | Normal birth weight (g) | Low birth weight (g) | Very low birth weight (g) |
| Australian Shepherd | >375 | 213-375 | <213 |
| Bichon Frisé | >181 | 163-181 | <163 |
| Cocker Spaniel | >280 | 142-280 | <280 |
| German Shepherd | >480 | 338-480 | <338 |
| Golden Retriever | >417 | 177-417 | <177 |
| Labrador Retriever | >406 | 248-406 | <248 |
| Maltese | >163 | 115-163 | <115 |
| Rottweiler | >410 | 345-410 | <345 |
| Shih Tzu | >176 | 128-176 | <128 |
| West Highland White Terrier | >190 | 129-190 | <129 |
| 👉🏽It is crucial to weigh newborn puppies at birth and daily throughout the neonatal period (from birth to 3-4 weeks of age), as consistent weight monitoring is a key indicator of their health and development. I recommend starting with kitchen scales (like this one), but for serious accuracy, consider this lab-grade scale, perfect for tracking puppy weights up to 5kg. |
| 👉🏽Neonatal growth charts are an excellent tool to quickly identify puppies with low birth weight, helping breeders and veterinarians take early action. These charts include data from over 115 different puppy breeds. Download them here! |
Implementing these steps promptly and effectively can significantly improve the outcomes for premature puppies by ensuring they receive the necessary care without delay.
Each action, from resuscitation to weighing, is a step towards stabilizing the most vulnerable newborns, allowing for immediate and appropriate interventions that can be life-saving.
In the past, it has been suggested that administering corticosteroids to newborn puppies might promote surfactant synthesis, as these steroids can accelerate lung development and enhance surfactant production, crucial for breathing.
Some veterinarians might still recommend this treatment, despite limited and inconclusive scientific literature on its effectiveness in canines.
Based on my experience, corticosteroid administration has not proven beneficial, and thus, I do not recommend this approach in current practice.
Feeding and Nutrition Tips
An essential focus for caregivers of premature puppies is to prevent the impacts of the 3-H syndrome, which includes hypothermia, hypoglycemia, and dehydration.
These conditions are especially critical in premature newborn puppies due to their increased fragility and reduced ability to regulate their body systems independently.
Hypothermia in premature puppies can occur rapidly as they lack the body fat necessary to insulate themselves and maintain body heat.
Hypoglycemia, or low blood sugar, is a common issue due to their inadequate glycogen stores and limited energy reserves, which are quickly depleted.
Dehydration is another risk, as these puppies might not nurse effectively, leading to insufficient fluid intake.
Given the severe risks associated with 3-H syndrome, it is crucial to provide an environment that helps manage these conditions effectively.
I have discussed detailed preventative and management strategies for each component of 3-H syndrome in previous blogs, which provide comprehensive guidelines on creating a supportive care framework for these vulnerable newborns.
For those looking for in-depth information on how to handle these critical care aspects, please refer to the detailed discussions in my previous blogs:
- Preventing Hypothermia in Newborn Puppies:
Newborn Puppies Temperature: The Critical Factor You Can’t Ignore
- Managing Hypoglycemia in Newborn Puppies:
How Much Karo Syrup for Newborn Puppies? Essential Tips for Hypoglycemia Prevention
- Preventing Dehydration in Newborn Puppies:
Newborn Puppy Won’t Nurse? Helpful Tips for Concerned Owners
An essential step for newborn puppies is to drink as soon as possible the first milk of their mother, the colostrum. Find out more about this in the following post:
Colostrum Secrets: Boosting Puppy Immunity and Growth from Day One
| 👉🏽 Here is the colostrum replacer I recommend for newborn puppies (where available). It’s especially beneficial for premature puppies, low birth weight puppies, and those born to females undergoing an elective C-section. |
| 👉🏽One essential tool to have on hand to prevent the 3H syndrome (hypoxia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia) in puppies is a high-quality milk replacer, ensuring they receive proper nutrition and energy support. Here is the milk replacer I recommend. It is also available through a professional program. Learn more about options in the USA and Canada. |
Monitoring Health and Development
Monitoring the health and development of premature newborn puppies is a crucial aspect of ensuring their survival and growth.
Recent data that I’ve incorporated into my presentations highlights several key metrics that are vital for breeders and veterinarians to monitor:
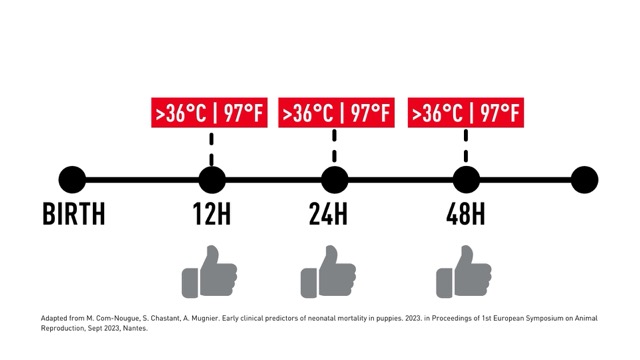
1. Temperature Monitoring: Maintaining an optimal body temperature in the first 48 hours post-birth is critical. A body temperature above 36 degrees Celsius (96.8 degrees Fahrenheit) during this period is considered a positive health indicator.
The slide below outlines the specific temperature ranges to aim for, ensuring puppies have the best start in life.
| 👉🏽 To ensure accurate temperature monitoring, I recommend using a pediatric digital thermometer like this one or an infrared thermometer like this one for a non-invasive option. Both are fast, reliable, and essential for tracking a newborn puppy’s health. |
| 👉🏽Maintaining the ideal temperature for newborn puppies is crucial for their survival and well-being. There are different options available, including a heating lamp for evenly distributed warmth (like this one), a heating pad with adjustable settings for targeted heat (like this one), or a pediatric incubator, which offers precise temperature and humidity control (like this one). Choosing the right option depends on your needs, but each plays a vital role in keeping your puppies warm and healthy. |
2. Blood Glucose Levels: Monitoring blood glucose levels in newborn puppies is now more refined than ever. It’s not just about detecting low levels but also about identifying neonatal hyperglycemia—a sign of stress that occurred during parturition. Elevated glucose levels can indicate the need for immediate veterinary intervention.
The slide below presents the newly established thresholds for blood glucose that can guide interventions more effectively.

| 👉🏽One essential tool to have on hand to prevent the 3H syndrome (hypoxia, hypothermia, hypoglycemia) in puppies is a high-quality milk replacer, ensuring they receive proper nutrition and energy support. Here is the milk replacer I recommend. It is also available through a professional program. Learn more about options in the USA and Canada. |
3. Weight Monitoring: Conventional wisdom once suggested that “it was normal for newborn puppies to lose up to 10% of their birth weight in the first 24 hours”. However, updated research and practices now tell us that puppies must consistently gain weight from the outset.
To monitor this effectively, you can use the following formula to calculate the growth rate at 24 and 48 hours:

This calculation will help determine whether the puppies are gaining weight at a healthy rate.
The following slide from my recent presentations outlines expected growth rates and what deviations might indicate about the health of the puppy.

Each of these monitoring steps is critical for ensuring the health of premature puppies.
By closely observing these indicators, caregivers can swiftly intervene when necessary, providing the best care to enhance the puppies’ chances of thriving.
| 👉🏽It is crucial to weigh newborn puppies at birth and daily throughout the neonatal period (from birth to 3-4 weeks of age), as consistent weight monitoring is a key indicator of their health and development. I recommend starting with kitchen scales (like this one), but for serious accuracy, consider this lab-grade scale, perfect for tracking puppy weights up to 5kg. |
| 👉🏽Neonatal growth charts are an excellent tool to quickly identify puppies with low birth weight, helping breeders and veterinarians take early action. These charts include data from over 115 different puppy breeds. Download them here! |
How Can Veterinary Interventions Help With Premature Puppy Deliveries?

One might wonder if there’s anything that can be done to prevent premature puppy delivery.
As we’ve explored, some causes of premature birth, such as luteal failure and pregnancy toxemia, can indeed be anticipated and managed with proper monitoring and care during pregnancy. These preventative measures are crucial for maintaining the health of both the mother and her puppies.
But what happens if, despite all precautions, a female dog starts to give birth prematurely? Is there a way to halt the labor process once it has begun?
This question taps into a critical area of canine obstetrics. While stopping labor is challenging and often not recommended due to potential risks to both the mother and puppies, certain interventions might be considered – under specific veterinary guidance obviously.
Recognizing the Onset of Labor in Breeding Dogs
For dog breeders, understanding and recognizing the signs of labor in a female dog is crucial, particularly to determine if the labor is premature.
The most common signs of a dog going into labor include nesting behavior, restlessness, loss of appetite, and a drop in body temperature. A female might also start licking her genital area frequently and could experience visible contractions and discharge.
If these signs are observed before the expected due date window—previously outlined based on accurate timing of ovulation using progesterone tests—it’s essential to consult a veterinarian immediately.
This professional evaluation can determine whether the labor is premature and what interventions may be necessary to ensure the health of the mother and puppies.
Emphasizing the importance of accurately predicting the window of parturition through progesterone testing cannot be overstated. This accuracy is key to preparing for the birth, understanding when labor is occurring prematurely, and deciding when to seek veterinary help.
| 👉🏽Activity monitors during gestation are game-changers, enabling us to detect the onset of labor and identify potential complications during pregnancy. In this critical period, there’s no doubt that an ounce of prevention is worth a pound of cure. My personal favorite? This one right here. The reason I am super excited about it is because they validated a Pregnancy Health Monitor that is in my opinion game-changing. Use code TMV_CARE for a 10% discount. |
Medical Options for Preterm Labor
In the realm of canine obstetrics, there exist medical protocols described in scientific literature aimed at delaying parturition, particularly through the use of medications known as “tocolytics.”
Tocolytics are drugs designed to suppress labor, providing a crucial intervention for cases of premature labor where prolonging pregnancy may benefit the health of the puppies.
However, it’s important to understand that such interventions should always be conducted under strict veterinary supervision.
In practice, the use of tocolytics in veterinary medicine is not widespread.
Often, by the time a female dog is brought to the veterinarian with signs of early labor, the process of parturition has already begun to a point where it might be safer and more practical to allow the birth to proceed. This is especially true if puppies have already started to be expelled, as intervening medically at this stage can pose additional risks to both the mother and her offspring.
For breeders whose dogs have a history of premature births, discussing these options with a veterinarian well in advance can be invaluable. Such discussions can help prepare for any potential complications associated with early labor, ensuring that every possible precaution and intervention strategy is considered to promote the health and well-being of both the mother and her puppies.
While prematurity in newborn puppies often carries a poor prognosis, preparation remains key in this field. Understanding the expected timing of birth is crucial, and should complications arise, we are now better equipped with structured approaches to optimize their chances of survival. I am hopeful that advancements such as the development of a canine synthetic surfactant will further enhance our ability to support these vulnerable lives in the future. Until such innovations become available, rest assured that we are more capable today than ever before in providing the necessary care for premature puppies, giving them a fighting chance to thrive.

One of the most common challenge we encounter in breeding kennels is NEONATAL MORTALITY.
It can be very frustrating… even heart-breaking.
Good news though : you can do something about it !
We now have more knowledge than ever in this discipline.
In recent years, new research brought us a much better understanding of what can be done to optimize the health of newborn puppies.
By taking this course, this is what you will learn indeed !
